

| Vol. III.—No. 105. | Published by HARPER & BROTHERS, New York. | price four cents. |
| Tuesday, November 1, 1881. | Copyright, 1881, by Harper & Brothers. | $1.50 per Year, in Advance. |
Every boy realizes the fascination of fishing, even if he gets nothing but bites—mosquito bites at that. It is the anticipation of what one may catch which heightens the every charm of the sport itself.
But taking flounders from the wharf, or trout in the mill-stream, is quite a different thing from cod or pollock fishing in thirty fathoms of green sea. The one may sometimes be the pursuit of pleasure under difficulties; the other is generally the pursuit of business under danger. So at least most of you would have said had you seen "the widow Buttles's Ben" at the time when my story begins.
He was standing upright in a fourteen-foot dory, and I may add that the dory, generally speaking, was also standing upright, which is not so surprising, for, in the first place, the wind was blowing half a gale; in the second place, Ben's boat was anchored, with fifty fathom of scope near the "Breaking Shoals," and by chart Breaking Shoals bear E.N.E. from Covert Point, distance three and a quarter miles, with nothing nearer than Europe to check the force of the Atlantic billows.
"No idea it was so late," muttered Ben, a little anxiously, as he began to reel up one of the lines. "Looks baddish to wind'ard, and the sea is getting up," he added, with a rapid glance from the cloud-bank behind which the sun had set to the heaving ocean about him. A landsman would have supposed that the sea had already got up. How Ben kept his balance so easily, as the dory "ran" on the slopes of the great waves, which slipped from under its flat bottom with such startling suddenness, would seem marvellous to any one except a person living alongshore. But Ben Buttles was perfectly at home in his dory; for in the little sea-board village of Covert, whose distant lights were just visible through the gathering darkness, every man owned some kind of a boat, while every other man was "Cap'n" or "Skipper." Hence the most that troubled Ben was the thought that he had been so taken up with fishing as to forget that the sun had begun to set, the tide to ebb, and a gale to rise.
"And I promised mother to be home by dark— Gorry-buster!"
This last untranslatable word was called forth by a tremendous tug at his other line, which he had just taken up.
"Why, I must have hooked on to an anchor," gasped Ben, as he pulled and panted. But an anchor would never have darted off like mad when it was near the surface, taking thirty or forty fathoms of his line before he could check it. And as Ben, who was sturdy and strong for his age, began to haul in his line by main force a fathom at a time, he well knew what it was he had hooked.
"I never caught one, but I know just how it's done," he said, setting his teeth firmly together, as the great fish, now nearly alongside, began to show signs of being exhausted by its struggles.
Holding his shortened line firmly in his left hand, Ben picked up his "gaff"—a short pole, to one end of which a stout hook is affixed. As the dory sank into a great chasm of water, he threw his weight on one side, pressing the gunwale level with the water, so that it almost touched the side of his finny prey. One dexterous movement of both hands and knees, and the halibut—for this was the kind of fish he had secured—was fairly "scooped" into the dory, where it was quickly stunned by a blow on the head.
Ben was exultant, but there was little time in which to pat himself on the shoulder. The gale had been growing and the gloom increasing while he was absorbed in his exciting sport. The dory was tugging at her "killock" like a mad thing, as though realizing the necessity for making an immediate change of base.
He lost no time in getting his anchor, with which he also got a thorough drenching, and began to pull vigorously toward Covert Light, which was streaming out through the storm and gloom. But, alas! hardly had he taken a dozen strokes when his starboard oar snapped off close to the blade, where he had spliced it the day before.
To think was to act with the widow's Ben. Backing water with the other oar to keep the dory "head on" for a moment, he drew it rapidly inboard. Seizing the end of the bow painter, he made a clove-hitch round the middle of the whole oar and the disabled one, lashing the two firmly together. Then, just as the dory was on the point of swinging broadside to the waves (in which case she would have capsized in a twinkling), he threw the whole arrangement over the weather bow.
The resistance of this temporary drag in the water brought the dory head on to the terrible sea, but Ben saw at a glance that she did not ride easy.
"Too much dead weight amidships," he said. And with a sigh he launched the big halibut over the rail, following it with the twenty or more large cod and pollock that he had also taken. This had the desired effect, and now the buoyant craft began to ride the great rollers, scarcely taking any water on board, except the spray blown from the wave crests by the force of the wind, which was now coming in heavy gusts from the northwest.
As Ben sat huddled in the dory's stern, his thoughts were not particularly cheerful. Not that he was utterly cast down, or had given up all hope of being saved—oh no, Ben Buttles was more than ordinarily courageous, or, as his mother used to say, "He was dretful ventur'some."
But he knew the chances were against him. He had forgotten it, but it suddenly occurred to him that it was the 18th of October, and this storm, therefore, was undoubtedly the "line gale." He was drifting seaward before it on the ebb tide, about three knots an hour. Even if the dory lived through the night, the prospect of being picked up next day in such a gale was very small. If anything happened to him, the two-hundred-dollar mortgage on the little brown house would never be paid, interest or principal.
"And mother would have to go," thought Ben, swallowing violently at a hard lump in his throat. For Mr. Travis, who held the mortgage, wanted to get their little house into his possession, and tear it down, that he might build a summer hotel on its site. Mrs. Buttles would have no one but God to look to if Benjie should be taken away. Husband and three sons were all sleeping under the billows. No wonder, then, that while her storm-tossed boy, recalling these things, was praying in his heart, "Lord, comfort and care for mother," she, kneeling by the bed-side at home, was crying out in agony, "Lord, save my boy."
Blacker grew the night, wilder the billows, and louder the voice of the storm. No boat that was ever built could live much longer in such a sea. The wave crests were constantly breaking over the dory's gunwale, forcing Ben to bail continually.
"She can't stand this much longer," said Ben, despairingly, as the dory rose on an awful sea, and he felt for a moment the full force of the gale. But what was the ghostly red glare which suddenly shone into Ben's white face through the gloom? What but the side-light of the brig Calypso, hove to on the starboard tack! And as a wild cry rose to the boy's lips, the dory was swept with terrible force against the black hull of the vessel itself, shattering the frail craft as though it had been made of egg-shell china.
Clutching frantically at the brig's smooth slippery sides as he was swept past, Ben's fingers grasped one of the iron chain-plates of the main-channel, as the brig sank in the[Pg 3] trough of the sea. Seizing its fellow with his other hand, he clung to it with a death-grasp. As the brig began slowly to rise on the great slope of black water towering above her, Ben summoned all his remaining strength. Half scrambling, half climbing, he pulled himself up on the weather-rail; from thence he was thrown inboard by a lurch of the brig, at the very feet of Captain Bob Adams. Captain Bob, who had been reared in the navy, was not only a cool man, but also a thorough disciplinarian. Ben's appearance was so sudden, and unexpected that Captain Adams took him for one of his own crew who had violated the rules of sea etiquette in coming aft on the weather-quarter, which is sacred to ship's officers alone. And as the boy scrambled to his feet, Captain Bob's energetic words surprised him even more than the fact of his own strange deliverance.
"But I couldn't help it, sir," shouted the bewildered Ben (for between the roar of wind and sea, one could hardly hear himself think), wiping the spray from his eyes; "I was laying to in my dory by a drag, and she drifted foul of the brig."
"Oh," replied Captain Bob, who was never known to express surprise at anything, "that was it, eh? Well, go below, and the steward will give you some hot coffee. Go to loo'ard, too," he roared, as Ben proceeded to obey.
The steward, who was a colored gentleman, grumbled at the order, but of course dared not refuse. And after Ben had swallowed a pint or so of the invigorating fluid, and got into a dry shirt and trousers furnished by the second mate, he began to feel perfectly at home. He found that the brig was from Bangor, Maine, bound to Savannah, in ballast.
"And likely enough it will moderate by to-morrow, so I can put you on board some in-bound fisherman," said Captain Bob, who, despite his gruff voice, was one of the kindest-hearted men in the world. But the mercury kept falling in the barometer, and the wind, suddenly veering round into the northeast, blew harder than ever before morning, and by daybreak there was nothing left but to "scud" before the heaviest gale that had visited our coast for years. Under a fore storm-stay-sail, close-reefed foretopsail and main stay-sail, the Calypso sped over and through the storm-tossed sea at a rate which made Ben hold his breath.
"You'll, have to make the voyage with us, youngster, whether or no," said the Captain, grimly, and Ben only nodded.
If his mother could have known of his safety, he would rather have enjoyed the novelty of the situation, for Ben was a born sailor. But there was no help for it, and he accepted the situation with the best possible grace. It is an ill wind that blows nobody good, and the equinoctial gale blew them clear by stormy Cape Hatteras before it was fairly exhausted. Then came the strong but steady breathings of the trade-wind to fill the Calypso's every sail. And ten days later, as Mrs. Buttles was dropping hot tears on some rusty bits of crape with which she was trimming her Sunday bonnet, she was nearly thrown into convulsions of joy by the receipt of a telegram reading thus:
"Savannah, October 28, 187-.
"Picked up by brig Calypso. Will write soon.
"Benjamin J. Buttles."
"For this an' all other mercies, thank the Lord!" reverently exclaimed the good woman, wiping her glasses. "But I do hope," she added, a moment later, "that Ben won't go to gettin' into no scrapes down to Savannah, for he's sech a dretful ventur'some creeter." Whether he did, and if so, how he did it, remains to be told in the next number.
Fully a million American boys have read one or more of Paul Du Chaillu's stories of African travel, and then, like Oliver Twist, demanded more; for the first civilized discoverer of the gorilla seemed to have a peculiar faculty for writing about just those things that boys enjoy. The wishes of these youthful readers are about to be gratified, and in very generous measure, for the author is soon to publish a book of nearly a thousand pages about a country almost as distant and little known by Americans as Equatorial Africa. The title of the work is The Land of the Midnight Sun, and from the numerous pictures it contains we have selected the two illustrations given on the next page.
The people of this wonderful land, which consists of Norway, Sweden, Lapland, and Finland, have comfortable homes, wear good clothes, and always have enough to eat; but between the climate, the shape of the land, and the fact that they see but little of either travellers or tramps, they have many customs that are unusual enough to seem sometimes funny, and always curious.
 A CHRISTMAS SCENE IN SCANDINAVIA.
A CHRISTMAS SCENE IN SCANDINAVIA.
The boys of Scandinavia have very good times; there is excellent fishing nearly everywhere, and water suitable for boating is not far distant from any home. In some parts of the country the water is frozen during nine months of the year, but in part of this time the skating is good, without any danger of the ice breaking; and when the snow hides the ice, it covers the hills—and such hills! High, steep, and well covered with snow, a hill in Norway or Sweden is the place of all places for coasting, for even on the roads there is very little danger of meeting a wagon while rounding a curve, or of dashing unexpectedly across a railroad track just as a locomotive comes thundering along. Besides, the favorite method of coasting over there is about ten times as exciting as that which is enjoyed here, for the boys descend hills on show-shoes. These shoes resemble the American snow-shoe about as closely as a miniature yacht resembles a chip with a splinter mast and paper sail. They are narrow instead of broad, so a person wearing them does not look awkward, or tire easily, and they are just about as long as their owners are tall. In using them the wearer slides his feet instead of lifting them, and if he wants to hurry, he pushes himself along with a couple of sticks, the lower ends of which are wrapped or shod so that they push against the surface of the snow instead of sinking into it. To descend a hill, the wearer places his feet close together, the shoes being exactly parallel, squats as low as possible, and lets himself go. If the hill is long and steep, he reaches the bottom about as rapidly as a bird could. This style of coasting seems so ridiculously easy that boys sometimes try it slyly rather than wait until their fathers can get time to teach them, and the usual results are a scratched face, and a general bruising all over. The least variation of either shoe from a position parallel to the other shoe is sufficient to cause all of these discomforts, and sometimes more, for occasionally when a boy leans forward a little too much in going over a snow-covered stone or other "bumper," he starts for a somersault which is only prevented by the toes of the shoes burying themselves in the snow, and suspending the boy by the feet with his face downward.
American boys who do not like to go to bed would in Northern Norway or Sweden imagine they had a capital excuse for sitting up, for no boy of spirit can endure to retire by daylight, and in a part of the far Northern summer daylight does not end at all during the twenty-four hours, and even during the month preceding and following this strange period there is only an hour or two of darkness. For a day or two the sun may be seen at midnight, and during several months the only way of discovering[Pg 4] bed-time is to look at the clock. This wealth of daylight has some disadvantages; for while it lasts, the mosquitoes never sleep at all, but attend strictly to business, and when they alight upon a toothsome boy, their conduct is gluttonous to a disgraceful degree. It is an unsettled question, however, whether the boys do not object even more to retiring during the winter nights, which are as long as the summer days. In midwinter, day dawns at eleven o'clock, and night follows within two hours; but the moon and stars shine brighter than they ever do here, and American boys would consider it sinful to waste such splendid opportunities for skating or sleighing.
The operation of dressing in cold weather in the far North is so elaborate that it is difficult to understand how a deliberate boy or girl in Lapland can be ready for breakfast before dinner-time. First, two suits of thick woollen under-clothing are put on, and over these goes a shirt of reindeer-skin, with cloth bands to fasten at the wrists; sometimes two of these shirts, or kaptas, are worn, and a reindeer-skin vest beneath them. The trousers are of reindeer-skin also. Two pairs of heavy woollen stockings are worn, and the child who puts these on when they are damp is sure to have trouble with his feet. Around the feet a peculiar grass, well dried, is carefully wound, and over all this goes the shoe. Buttons and hooks and eyes are scarce in Lapland; all clothing is fastened by strings, and it is dreadful to think of all the "hard knots" that Lapp children have fumbled over while too sleepy to be amiable.
 REINDEER AND PACK, WITH LAPP DRIVER.
REINDEER AND PACK, WITH LAPP DRIVER.
One special distinction is enjoyed by the Lapp boy and girl over all other children in the world: each is sure of owning a reindeer if the family live in the reindeer region. When a child is born, a deer is set apart for him at once, and by the time the pride of the family is old enough to drive, his animal will have been trained for him. How much time and trouble this training has cost, the boy never can realize until he becomes a man, and breaks deer to harness himself. It would seem to any sensible person that as the harness consists only of a collar, a thong (or trace), and a single rein, the animal might easily become accustomed to them, particularly as the sleigh has neither pole nor shafts; but the deer does not regard the subject in the same light. He forgets whatever he learns, just as if he were a lazy school-boy. Even after two years of education he seldom can be depended upon to do the right thing at the right time.
It would never do to tell a Laplander the story of Santa Claus's famous team of reindeer, for as one of the species is all that a skillful driver can manage, how could any old fellow manage so many? The only point of resemblance between a reindeer sleigh and other sleighs is that they are all made to run on the snow, for the Lapp sleigh is really a boat, short, narrow, and graceful, and it rests on a broad keel instead of two runners. It closely resembles in appearance and size one-half of a canoe. It holds but one person, who must divide his attention between driving the deer and[Pg 5] acting as ballast. The driving is the easiest part of the work, because when the animal is fairly started, he goes straight ahead, and there are no street corners in Lapland. There are curves, however, and as a spirited deer will travel fifteen miles an hour, and can not be coaxed to slacken his speed, it is about twice as hard to keep the sleigh on a level keel in rounding a well-beaten curve of the road as to avoid capsizing while "jibing" a small boat in a brisk breeze. The reindeer makes no trouble in the stable, for he never enters one. He prefers to find his own food, which consists almost entirely of moss. This may be under the snow, but he knows how to dig his way down to it; and if the snow is deep, the only way of finding a deer that is wanted is to go from hole to hole. As the moss grows very slowly, moving-days are frequent in Lapp families, for the people must go wherever the deer can find food.
To juvenile collectors of antiquities and curiosities, Scandinavia is the rarest land in the world. Not only are there many arrow-heads, something like those once used by the American Indians, but the swords, shields, spears, and armor of the earlier inhabitants are often found. But the list does not end with these: Wisby, a Swedish city, was many hundred years ago the centre of trade in Northern Europe, and many thousands of coins and jewels found there came from far-away places like Greece, Rome, Persia, and India. Still more, the famous sea-rovers, known as Northmen or Vikings were mostly from Norway and Sweden, and when they went on expeditions to other countries, they were as industrious as the Greeks and Romans, or, later, the French, English, and Spanish explorers, in carrying home whatever was worth stealing.
But many numbers of Young People might be filled with stories of what Mr. Du Chaillu saw, heard, and enjoyed. Every part of the country is described: the wonderful fiords, or bays, that were hollowed from lofty mountains by great glaciers; the castles and palaces that were built when Sweden was so rich and powerful that all Europe feared her; the feasts that last for days, and the Christmas fun that is kept up for a fortnight—are all described in the entertaining manner which has made the author so well known among boys. Instead of hurrying from one point to another, Mr. Du Chaillu travelled leisurely, and thus he saw and heard a great deal that will be new even to people who have visited Scandinavia, and imagine that they know all about it.

ut to return to Ni-ha-be and Rita, whom we left sitting with Mother Dolores in Many Bears' lodge. It was a large round tent that they were sitting in, upheld by strong slender poles that came together at the top so as to leave a small opening. On the outside the covering was painted in bright colors, with a great many rude figures of men and animals. There was no furniture, but some buffalo and bear skins and some blankets were spread upon the ground, and it was a very comfortable[Pg 6] lodge, for any weather that was likely to come in that region.
In such a bright day as that, all the light needed came through the open door, for the "flap" was still thrown back. The two girls, therefore, could see every change on the dark face of the great chief's Mexican squaw.
A good many changes came, for Dolores was very busily "remembering," and it was full five minutes before the thoughts brought to her by that picture of the "Way-side Shrine" began to fade away, so that she was again an Indian.
"Rita," whispered Ni-ha-be, "did it say anything to you?"
"Yes. A little. I saw something like it long ago. But I don't know what it means."
"Rita? Ni-ha-be?"
"What is it, Dolores?"
"Go. You will be in my way. I must cook supper for the chief. He is hungry. You must not go beyond the camp."
"What did the talking leaf say to you?" asked Ni-ha-be.
"Nothing. It is a great medicine leaf. I shall keep it. Perhaps it will say more to Rita by-and-by. Go."
The Apaches, like other Indians, know very little about cookery. They can roast meat and broil it, after a fashion, and they have several ways of cooking fish. They know how to boil when they are rich enough to have kettles, and they can make a miserable kind of corn-bread with Indian corn, dried or parched and pounded fine.
The one strong point in the character of Dolores, so far as the good opinion of old Many Bears went, was that she was the best cook in his band. She had not quite forgotten some things of that kind that she had learned before she became a squaw. Nobody else, therefore, was permitted to cook supper for the hungry chief. It was a source of many jealousies among his other squaws, but then he was almost always hungry, and none of them knew how to cook as she did.
She was proud of it too, and neither Ni-ha-be nor her adopted sister dreamed of disputing with her after she had uttered the word "supper."
They hurried out of the lodge, therefore, and Dolores was left alone.
She had no fire to kindle. That would be lighted in the open air by other female members of the family.
There were no pots and saucepans to be washed, although the one round, shallow, sheet-iron "fryer," such as soldiers sometimes use in camp, which she dragged from under a buffalo-skin in the corner, would have been none the worse for a little scrubbing.
She brought it out, and then she dropped it and sat down to take another look at that wonderful "talking leaf."
"What made me kneel down and shut my eyes? I could remember then. It is all gone now. It went away as soon as I got up again."
She folded the leaf carefully, and hid it in the folds of her deer-skin dress, but she was evidently a good deal puzzled.
"Maria Santisima—yes, I do remember that. It will all come back to me by-and-by. No! I don't want it to. It makes me afraid. I will cook supper, and forget all about it."
A Mexican woman of the lower class, unable to read, ignorant of almost everything but a little plain cookery, has less to forget than have most American children of six years old. But why should it frighten her, if the little she knew and had lost began to come back to her mind?
She did not stop to answer any such questions as that, but poured some pounded corn, a coarse uneven meal, into a battered tin pan. To this was added a little salt, some water was stirred in until a thick paste was made, and then the best cook of the Apaches was ready to carry her batter to the fire. Envious black eyes watched her while she heated her saucepan on the coals she raked out. Then she melted a carefully measured piece of buffalo tallow, and began to fry for her husband and master the cakes no other of his squaws could so well prepare.
When the cakes were done brown, the same fryer and a little water would serve to take the toughness out of some strips of dried venison before she broiled them, and the great chief would be the best-fed man in camp, until the hunters should return from the valley below with fresh game.
They were quite likely to do that before night, but Many Bears was a man who never waited long for something to eat after a hard day's march.
If Dolores had been a little alarmed at the prospect of being forced to "remember," a very different feeling had entered the mind of Rita when she and her sister came out of the lodge.
"What shall we do, Ni-ha-be?"
"Red Wolf told me he had something to say to me. There he is now. He beckons me to come. He does not want you."
"I am glad of it. There are trees and bushes down there beyond the corral. I will go and be alone."
"You will tell me all the talking leaves say to you?"
"Yes, but they will talk very slowly, I'm afraid."
Even the harsher sounds of the Apache tongue had a pleasant ring in the sweet, clear voices of the two girls, and the softer syllables, of which there were many, rippled after each other like water in a brook. It seemed, too, as if they said quite as much to each other by signs as by words. That is always so among people who live a great deal out-of-doors, or in narrow quarters, where other people can easily hear ordinary conversation.
The one peculiar thing about the signs used by the American Indians is that they mean so much and express it so clearly. Men of different tribes, not able to understand a word of each other's spoken tongue, will meet and talk together by the hour in "sign language," as intelligently as two well-trained deaf-mutes among the whites.
Perhaps one reason more for so much "sign-talking" is that there are so many tribes, each with a very rough tongue of its own, that is not easy for other tribes to pick up.
Red Wolf was again beckoning to Ni-ha-be, and there was an impatient look on his dark, self-willed face. It was time for her to make haste, therefore, and Rita put the three magazines under the light folds of her broad antelope-skin cape, and tripped away toward the bit of bushy grove just beyond the "corral."
What is that?
In the language of the very "far West" it is any spot or place where horses are gathered and kept, outside of a stable.
 THE CORRAL.
THE CORRAL.
The great Apache nation does not own a single stable or barn, although it does own multitudes of horses, ponies, mules, and even horned cattle. All these, therefore, have to be "corralled," except when they are running loose among their unfenced pastures; there are no fences in that part of the world any more than barns.
Immediately on going into camp the long train of pack mules and ponies had been relieved of their burdens, and they and most of the saddle-horses had been sent off, under the care of mounted herders, to pick their dinners for themselves in the rich green grass of the valley.
Chiefs and warriors, however, never walk if they can help it, and so, as some one of them might wish to go here or there at any moment, several dozens of the freshest animals were kept on the spot between the camp and the grove, tethered by long hide lariats, and compelled to wait their turn for something to eat.
There was a warrior on guard at the "corral," as a matter of course, but he hardly gave a glance to the pretty[Pg 7] adopted daughter of Many Bears as she tripped hurriedly past him. It was his business to look out for the horses, and not for giddy young squaws who might find "talking leaves."
Rita could not have told him, if he had asked her, why it was that her prizes were making her heart beat so fast as she held them against it.
She was not frightened. She knew that very well. But she was glad to be alone, without even the company of Ni-ha-be.
The bushes were very thick around the spot where she at last threw herself upon the grass. She had never lived in any lodge where there were doors to shut behind her, or if she had, houses and doors were alike forgotten; but she knew that her quick ears would give her notice of any approaching footsteps.
There they lay now before her, the three magazines, and it seemed to Rita as if they had come on purpose to see her, and were looking at her.
No two of them were alike. They did not even belong to the same family. She could tell that by their faces.
Slowly and half timidly she turned the first leaf; it was the cover-leaf of the nearest.
A sharp exclamation sprang to her lips. "I have seen her! Oh, so long ago! It is me, Rita. I wore a dress like that once. And the tall squaw behind her, with the robe that drags on the ground, I remember her too. How did they know she was my mother?"
Rita's face had been growing very white, and now she covered it with both her hands, and began to cry.
The picture was one of a fine-looking lady and a little girl of it might be seven or eight years. Not Rita and her mother, surely, for the lady wore a coronet upon her head, and carried a sceptre in her hand, but the little girl looked very much as Rita must have looked at her age. It was a picture of some Spanish princess and her daughter, but like many pictures of such people that are printed, it would have served as well for a portrait of almost anybody else. Particularly, as it seemed to Rita, of herself and her mother.
"He is not there. Why did they not put him in? I loved him best. Oh, he was so good to me! He had plenty of talking leaves, too, and he taught them to speak to me. I will look and see if he is here."
Rita was talking aloud to herself, but her own voice sounded strange to her, with its Indian words, and ways of expression. She was listening without knowing it for another voice, for several of them, and none of them spoke Apache.
She turned leaf after leaf with fluttering haste in her eager search for that other face she had spoken of.
In a moment more she paused, as the full-length picture of a man gazed at her from the paper.
"No, not him. He is too old. My father was not old. And he was handsome, and he was not dark at all."
She shut the book for a moment, and her face was full of puzzle and of pain.
"I said it. I was not talking Apache then. And I understood what I was saying."
She had indeed, when she mentioned her father, spoken pretty clearly in English.
Was it her mother-tongue, and had it come back to her?
She turned over the leaves more eagerly than ever now, and she found in that and the two other magazines many pictured faces of men of all ages, but each one brought her a fresh disappointment.
"He is not here," she said, mournfully, "and it was he who taught me to—to—to read—books."
She had found two words now that were like little windows, for through them she could see a world of wonderful things that she had not seen before—"read" and "books."
The three magazines were no longer "talking leaves" to her, although they were really beginning to talk. Her head ached, and her eyes were burning hot, as she gazed so intently at word after word of the page which happened to be open before her. It was not printed like the rest. Less closely, and not in such a thronging mass of little black spots of letters. It was a piece of very simple poetry, in short lines and brief stanzas, and Rita was staring at its title.
The letters slowly came to her one by one, bringing behind them the first word of the title; but they seemed to Rita to be in her own brain more than on the paper. It was a hard moment for Rita.
"He made me say them one word at a time. He was so good to me! Yes, I can say them now. I know what they mean. Oh, so long ago! so long ago!"
There was no longer any doubt about it. Rita could read English. Not very easily or rapidly at first, and many of the words she came to puzzled her exceedingly. Perhaps some of them also would come back to her after a while. Some of them had always been strangers, for the very brightest little girls of seven or eight, even when they read well, and have their fathers to help them, are but at the beginning of their acquaintance with "hard words."
"I shall know what the pictures mean now. But I will not tell anybody a word about it. Only Ni-ha-be."
This is the song the miller sang,
The selfish miller of Dee:
"I care for nobody, no, not I,
And nobody cares for me."
He ate and drank, and worked and slept,
Money and land had he,
But never a poorer mortal slept
Than the selfish miller of Dee.
The village maids grew good and fair,
But they grew not near his life;
His hearth-stone only held one chair—
He had no room for a wife.
No woman's footstep, quick and light,
Came down the silent stair
To bless him every morn and night
With kisses unaware.
The village lads and lasses knew
The charm of the old mill-race;
Oh, what a happy little crew
Oft made it their playing-place!
But none of them climbed the miller's knee
When the evening shades fell dim;
He cared for nobody, no, not he,
And nobody cared for him.
So he lived alone, he had no kin;
And in all the country-side
There wasn't a mortal cared a pin
Whether he lived or he died.
The women gave him never a smile,
The men had nothing to say,
No friend e'er crossed his garden stile,
No stranger wished him good-day.
He lived alone, and he died alone,
So his selfish life was sped;
They found him cold on his cold hearth-stone—
The miller of Dee was dead.
And no one cared to see his face,
No eye for him grew dim;
He cared for nobody, no, not he,
And nobody cared for him.
To share our life is to double our life;
And what if it double its care?
Loving can lighten the hardest strife,
Loving can make it fair.
Better to love, though love should die,
Than say, like the miller of Dee,
"I care for nobody, no, not I,
And nobody cares for me."
 "THE TWO FAMILIES."—From the Painting by Michael Munkacsy.
"THE TWO FAMILIES."—From the Painting by Michael Munkacsy.
I have a friend who is a very busy woman, but she reads many good books, knows what is going on in the world, and manages to do a great deal of very beautiful fancy-work. One day I asked her how it happened that she accomplished so much more than some other people could, and she said, "Oh, I look out for the odd minutes."
I have no doubt that among my readers there are girls and boys who have so much real work to do that they have not a great deal of leisure. Johnny finds weeding and hoeing very tiresome, and as for wood-chopping and the running of errands, he has his full share of both. Sophy, too, would have good times if it were not that there is always the baby to be taken care of, the old sheets to be turned, the parlors to be dusted, or the messages to be carried to the minister's wife.
How both John and Sophy, and ever so many other young people, dislike kind old ladies and gentlemen, who have a way of glaring at them through their spectacles, and observing: "Dear, me! how you grow, to be sure! You must be quite a help to your mother by this time." Or, worse still, they inquire about the school and the studies, and propose some problem or other in mental arithmetic quite different from anything in the book. Now please don't think Aunt Marjorie is that sort of an old lady, or has any greater liking for that sort of old gentleman than you have, children. But listen to her advice. Suppose for the next month you keep a definite bit of work on hand just for odd times. Let it be a volume of history, and read it in the nows and thens when you are waiting for father to finish a note; let it be a piece of embroidery or crochet-work, and take it up when there is time for only a few stitches at once. At the end of the month you will be surprised to see how much you have gained by using these odd minutes.
"I do dislike to introduce people to each other," said Eva to me one day last week.
"Why, pray?" I asked. "It seems to me a very simple thing."
"Well, when I have it to do, I stammer and blush, and feel so awkward, I never know who should be mentioned first, and I wish myself out of the room."
"I think I can make it plain to you," I said. "You invite Mabel Tompkins to spend an afternoon with you. She has never been at your home before, and your mother has never met her. When you enter the sitting-room, all you have to do is to say, 'Mother, this is my friend Mabel; Mabel, my mother.' If you wish to be more elaborate, you may say to your aunt Lucy, 'Aunt Lucy, permit me to present Miss Mabel Tompkins; Miss Tompkins, Mrs. Templeton.' But while you introduce Mabel to your father, or the minister, or an elderly gentleman, naming the most distinguished personage first, you present your brother, his chum, and your cousin Fred to the young lady, naming her first. Fix it in your mind that among persons of equal station the younger are introduced to the older, and that inferiors in age, position, or influence are presented to superiors. Be very cordial when, in your own house, you are introduced to a guest, and offer your hand. If away from home, a bow is commonly sufficient recognition of an introduction. Please, in performing an introduction, speak both names with perfect distinctness."
 "WHAT YER LAUGHIN' AT?"—From a Painting by Philip B. Haus.
"WHAT YER LAUGHIN' AT?"—From a Painting by Philip B. Haus.
I wonder how many of the children who roast chestnuts or duck for apples on All-hallow-eve have any idea how venerable are the games they play, or how, all the world over, young people are amusing themselves in pretty much the same fashion? In England, girls are strewing the ashes that are expected, though vainly, I fear, to spell the names of whoever loves them best. In Scotland, they are slyly sowing the hemp that their future husbands must come and gather. In Germany, they are making merry efforts to learn their fate with the help of the looking-glass that hangs by their bed. And many of these sports have been played for centuries, and were old even at the time of my story.
More than eighty years ago three little English children were solemnly arranging their mystic games for All-hallow-eve. They were alone in a tiny cottage, nearly half a mile from any neighbor, for father and mother had gone to the town of Ware, taking the baby with them, and would not be back before the next night; so Rupert, Margery, and little Nance, left to each other's company, were preparing without a shadow of fear to amuse themselves in their own fashion. Two big lumps of lead were ready to be melted, and then poured into water, there to assume hundreds of quaint little shapes; the chestnuts, carefully matched and named, were hopping gayly about on the fire-place; and half a dozen rosy-cheeked apples floated tantalizingly in a tub of water, waiting for a courageous diver.
Rupert, a strong and active boy of twelve, captured his apple at every plunge, thrusting his curly head fairly into the tub, and never bringing it out until his teeth were firmly fixed in its glossy sides; Margery, who did not fancy getting wet, only nibbled at hers, and sent it bobbing about the surface of the water; while poor little Nance would dive boldly down, and come up gasping and choking, her blue eyes tight shut, the water streaming from her fair hair, and looking more like a half-drowned kitten than a little girl who had not succeeded in catching a slippery apple.
"It's no use, Nance," said her sister; "you will never get one, if you keep on soaking yourself all night. Let us see now who will be married and who will die. Rupert, you go into the garden, and bring me in some earth on a plate, while I get the ashes and water."
The boy took a dish of yellow stone-ware, and went out to dig up the mould. It was a clear night, but blowing hard, and wild scraps of cloud came flying before the face of the moon, while to his left he saw the white banks of the river Lea, and could hear the rush of the waters as they swept angrily by. How high the river looked! thought Rupert, watching it, trowel in hand, and how loudly it sounded. He had never seen or heard it like that before, and for a moment he stood wondering what had caused this sudden rise. Then Margery's voice calling for the earth made him forget all about it, and in another minute he was back in the warm, bright kitchen, without a thought of the foaming torrent outside.
The little girl placed side by side on the table the three dishes; one of which held the mould, the other ashes, and the third clear water. Then she bound a handkerchief tightly over Nance's eyes, and after turning her around a couple of times to bewilder her, bade her go and put her hand in one of the plates. If she touched the water, she would be married; if her fingers wandered into the ashes, she was doomed to be an old maid; but if she reached the earth first, then she would surely die before the next All-hallow-eve.
Fully impressed with the solemnity of this awful rite, Nance slowly groped her way to the table, and after a moment's indecision put her little fat fingers softly down, when plump they went right into the water. Margery gave a shout of pleasure, and with a sigh of profound relief that her future was so securely settled, Nance unbound the handkerchief and handed it over to her sister. But with her matters were not so promising, for advancing with a great show of confidence, her evil genius led her straight to the ashes, greatly to her own disgust and Rupert's undisguised delight. It was his turn now; but just as his eyes were being bandaged, little Nance called out, "Look! Margery, look! the floor is all wet!"
With a bound the boy sprang to the door and opened it. Nothing but water met his eyes—water as yet but a couple of inches deep, but which was softly, steadily rising in the moonlight, while the rush of the river sounded now as if it were close by his side. In an instant he realized what had happened. The Lea, swollen by heavy rains, had overflowed its banks, and the water was gaining on them fast. Already it had entered the room where the frightened children stood, only half understanding their great danger.
"Go up stairs," shouted Rupert to his sisters; "and if the flood rises that high, we will climb out on the roof. Go quick!"
But Margery stood still, her brown eyes filling with tears. "Oh, Rupert," she cried, "the poor little baby ducks and chickens! They will all be drowned; and what ever will mother say when she comes back?"
Rupert never heeded her. The water by this time reached to their ankles, and to close the door was impossible. Thoroughly alarmed, he drew the little girls up the ladder-like staircase into their low attic. It would not take long for the waves to mount that high, and their only hope of safety lay in climbing on to the steep sloping roof. Opening the window, he crawled cautiously out, and then helped Nance and Margery to follow him. Side by side stood the three children, and saw the sullen waters, white and foaming in the moonlight, surge and sway around them. Where could they look for help? Their father gone, their neighbors ignorant that they were alone in the house, and perhaps in the general terror forgetting all about them. Abandoned in their great peril, with only a boy of twelve to aid and save them!
Poor little Nance sobbed and shivered as she crept closer to her brother's side; Margery, bewildered with fright, stood as if frozen into stone; but Rupert, with fast-beating heart and a despairing light in his blue eyes, watched the cruel waters as they rose, and tried to think how best to act for his sisters' sake and for his own. He could hear in the distance cries and shouts, and could see bonfires blazing on many roofs—signals of the common danger. He knew that along the outskirts of the town, and through the scattered parish of Ware, relief boats were even now rowing from house to house to save those who lived in cottages too low to shelter them. He called until he was exhausted, but the only answer was the sullen roar of the Lea and the beating of the waves around him. Already they were lapping against the attic windows. Something must be done, and quickly, if he would save his sisters from perishing.
"Margery," he said at last, "would you be very much afraid to stay here alone with Nance, while I try and get some help?"
"Oh, Rupert!" shrieked the child, throwing her arms around him, "you would surely be drowned, and so would we. What can you do in such an awful flood?"
"I could try and swim to the manor farm," said the boy. "It is not more than half a mile off at furthest, and there are plenty of floating boughs and fences in the water to rest me if I tire out. Margery, I must go, or we shall all drown together; and you know," he added, with a sob, "I promised father that I would take care of you."
"But to leave us here alone! Oh, Rupert, I should die!"
But Rupert's mind was made up. "It must be done at once," he said, "or it will be too late. Margery, try and be a little brave, and keep tight hold of Nance if the waves reach you before I can come back. Please God, I will save you yet." Then throwing off his shoes and jacket, he said once more, "Remember to keep tight hold of Nance," and plunged into the seething waters, in which no man could hope to live.
Margery's shriek died into silence, and clutching her little sister, she watched the slight figure tossed on the cruel billows as the boy swam bravely on. How long could his young strength avail against their mighty power?
In a minute he was swept out of sight, and with an awful feeling of loneliness, she crouched on the roof, holding Nance in her arms. Each moment passed slowly as an hour, while the waves crept ever higher and higher, until they washed against the children's feet as they clung closely together. What had become of Rupert? What would become of them? Nance's sobs were hushed from sheer exhaustion, and she only moaned and shivered slightly when the crawling water gained on them inch by inch. Some of her brother's courage had entered Margery's breast in this extremity of peril, and mingling with her broken prayers for aid were words of comfort to her little sister.
But every minute it became plainer to her that they could not keep their hold much longer. Chilled to the heart, their stiffened arms were gradually relaxing. The morning was beginning to break, and its dull gray light showed her nothing but the angry waves on every side. Familiar landmarks were all gone, and the child's lonely heart grew despairing in the midst of so much desolation. All hope was dying fast, when far in the distance came a dark speck, moving steadily over the solid waters, and growing larger and clearer every moment. It was a boat rowed by strong arms that shot forward to help them.
"Nance! Nance!" she sobbed, "they are coming! they are coming! Rupert has sent them, after all. He has saved us, as he said he would."
Another minute, and the two cramped and wearied little figures were lifted down from their perilous resting-place, and laid gently in the boat, Nance hardly conscious, but Margery trembling with the question she scarcely dared to ask.
"Where is Rupert?" she cried. "He sent you, I know; but where is he now?"
The men, two laborers from the manor farm, looked at each other with troubled eyes, but made no answer. Margery's pitiful glance wandered from one down-cast face to the other, as she strove to understand what this silence meant.
"He must have sent you to us," she said, slowly, and as if talking to herself; "else how would you have thought to come?"
"Ay, that he did," answered one of the rowers. "He sent us truly, but he spoke no words to tell his tale. If we had not been a parcel of frightened fools, we would have remembered you before."
He stopped, and Margery looked at him with dazed and startled eyes. As gently as he could he told her how, two hours before, the drowned body of a little fair-haired boy had been swept by the torrent past the windows of the manor farm. Every effort had been made to bring back some spark of life, but it was too late. Struggling alone through the night in the great waters, the child's slight strength had long since given out, and the waves tossed their light burden hither and thither in cruel sport. He had striven with all his might, for his sisters' sake, and he had rescued them; for when the little dead body was recognized, all remembered the helpless family in the cottage cut off from any assistance, and a boat was sent out instantly for those who might still be alive. Here they were, just in time, and Margery and her little sister were that day restored safe and well to their mother's arms.
And long years after, when children of her own gathered around her knee, Margery would tell them on each All-hallow-eve the story of that dreadful night, and of their brave little uncle Rupert, who with boyish courage had risked and lost his life to save the sisters committed to his care.
We once had a piping bullfinch that was given to my mother as a birthday present. Bully was very tame, and used to fly about the room every morning, settling now and then upon somebody's head; but he loved his mistress much more than any one else, and was never so happy as when perched on her shoulder, piping his little song, or pecking seeds from her lips. He once showed his love for her in a very pretty way. She had spent several days away from home, which made poor Bully very dull and sad, and returning late one evening, long after children and birds had shut their eyes for the night, went into the room, and spoke to him. Bully woke up, and was so delighted at the sight of his mistress that he at once began piping his tune in joyful welcome to her. The poor little bird had a sad end. It is, I believe, a well-known fact that bullfinches often die of grief or jealousy, but we did not know it at the time; and when we had the large cage of birds, our pretty bright Bully was put into it. He was so much vexed at seeing them share his mistress's attention that he sickened and died in a few days.
One summer we noticed that regularly every morning when the dining-room window was open, a small wasp used to fly in, generally with something in its mouth, and settle on the writing-table. On the side of the table nearest the window there were only sham drawers; but they had key-holes, and into one of them the wasp always crawled, coming out again in a few minutes, and flying away. But it was sure to come back several times, and occupy itself very busily in the hole. In a few days a little white wall gradually rose up in front of the opening, and at last quite closed it, as though it had been built up with a fine cement. About the same time several other key-holes in different parts of the house were closed in this manner, and that so effectually, that no key could be introduced into them. We once opened one with a sharp-pointed instrument, and found inside some fat green caterpillars. The wasp had laid its eggs inside the little house, and imprisoned the caterpillars to serve as food for its young ones as soon as they were hatched. We often wondered how the caterpillars lived so long, when there was apparently no food provided for them. But I have since read in some book of natural history that the wasp, when carrying them by their necks to their prison, sends them into a kind of stupor, which, fortunately for themselves, lasts until the end of their lives.
A window containing a collection of healthy and blooming plants stamps the owner as one possessing refined tastes and a kind disposition, together with a love for all that is beautiful in nature. Window boxes ornamented with English or American tiles, and lined inside with zinc, are too costly for the size of young people's pockets. Besides, there does not begin to be as much fun[Pg 12] in a "store" window box as is contained in one made at home with the assistance of father or big brother.
A well-made window box for the cultivation of plants during the winter and summer months will last a number of years with ordinary care.
 Fig. 1.—WINDOW BOX COMPLETE.
Fig. 1.—WINDOW BOX COMPLETE.
Fig. 1 represents a home-made window box when completed. The box consists of well-seasoned one-inch white pine thoroughly nailed together. At one end of the box (A) a hole is bored to allow all surplus water to drain off and into the pan, also shown at A. To prevent the water and moisture contained in the soil from rotting and warping the wood-work, several coats of hot asphalt are applied with an old paint-brush—asphalt varnish will also answer—thus closing up all possible leaks, and thoroughly protecting the wood-work. There is no rule for the proportion of window boxes; the requirements of the plants used and the widths of windows and sills govern the proportion of the boxes. If the windows intended for boxes are very wide, braces of wood should be fastened across the tops and bottoms of the boxes to strengthen them, and extra feet nailed on to support them.
All boxes as well as flower-pots containing growing plants should have a thorough "bottom drainage." This is accomplished by placing on the bottom of the box a layer of broken earthenware or old bones broken into small pieces. The bones answer a double purpose, that of drainage and a supply of plant food (ammonia, etc.).
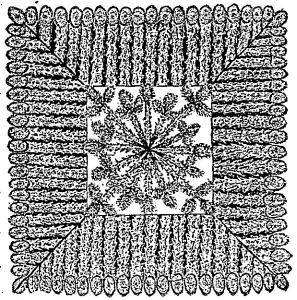 Fig. 2.—SPRUCE-WOOD PANEL.
Fig. 2.—SPRUCE-WOOD PANEL.
Fig. 2 is a spruce-wood panel. A square is first drawn on the outside of the window box; this square is painted a light green, to contrast with the brown of the spruce twigs. After the paint has dried, the guide lines are ruled from corner to corner through the centre. Small twigs of dried spruce-wood of a uniform thickness (about that of a lead-pencil) are selected. If the leaves do not fall off readily, the twigs are placed in an oven and thoroughly dried, so that they fall off at the slightest touch. The twigs are bevelled at the ends, as shown in the engraving. In the centre of the panel is nailed a square of wood equal in thickness to the spruce-wood twigs. This square is painted white, and is also ornamented with spruce twigs and the small cones of the spruce, the intention being to produce an elevated centre to the panel. The spruce twigs are firmly fastened with small brads. Over all two or three coats of furniture varnish are applied to develop the rich colors of the spruce-wood, as well as to protect it from outside moisture.
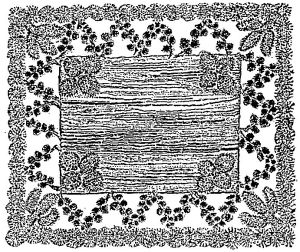 Fig. 3.—CONE PANEL.
Fig. 3.—CONE PANEL.
Fig. 3 is a cone panel. The outer border is composed of the burrs of the liquid-amber tree ("alligator-wood"), with corners of pine cones. The next line consists of a band of spruce branches with the cones attached. The centre is a sheet of white-birch bark, with hemlock cone corners. The ground consists of two coats of paint of a cream-white tint. The cones are fastened on with small brads, or pins that have been shortened to a convenient length.
 Fig. 4.—GRAPE-VINE PANEL.
Fig. 4.—GRAPE-VINE PANEL.
Fig. 4 is a tasteful grape-vine panel. The canes are first softened in boiling water or steam to make them pliable for bending into curves. The shorter curved branches consist of short sections neatly joined to the leading curves. The centre is composed of a frame-work of liquid-amber wood, with grape-vine monogram or other device. The grain of the white pine when brought out with the varnish answers for a groundwork.
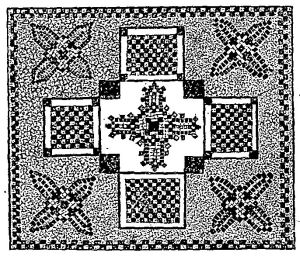 Fig. 5.—OIL-CLOTH PANEL.
Fig. 5.—OIL-CLOTH PANEL.
Fig. 5 is a panel covered with marbled oil-cloth (such as is used for covering tables and desks) of a light tint. It is first cut exactly the size of the panel, on which it is glued, the edges being secured by nailing on to them narrow[Pg 13] strips of floor oil-cloth of a checkered or vine pattern. The corner pieces and centre consist of simple and neat patterns in oil-cloth, but rich in contrasts of colors. Brilliant oil-colors can be used for borderings and framing in lines; intense blacks, reds, and whites are best. Over all, a coat of varnish is applied. In Fig. 6, the materials consist of "clinkers," or slag, from furnaces, stoves, glass-house furnaces, and iron foundries. These are fastened to the wood-work of the box by means of hot asphalt.
 Fig. 6.—CLINKER PANEL.
Fig. 6.—CLINKER PANEL.
The corner-pieces in the illustration are composed of clinkers of a light color. The central group consists of vitrified clinkers from an iron foundry or glass-house. The handsomest clinkers are to be obtained from glass-houses, as they are composed of more or less glass of different colors.
After the groups of clinkers are firmly fastened in position, a coating consisting of varnish, mixed with any of the chrome greens is applied to all parts of the exposed wood-work. The clinkers look much more brilliant when touched up here and there with gold or copper bronze. This is accomplished by applying varnish to the clinkers, which before it dries, touch on the bronze with a clabber of cotton or wool.
 Fig. 7.—MOSAIC PANEL.
Fig. 7.—MOSAIC PANEL.
Fig. 7 consists of cross sections of various kinds of woods, which are well seasoned previous to being glued together.
Straight branches of red cedar, black walnut, red birch, etc., etc., are selected; these are cut into uniform lengths, and tightly bound together with strong cord or wire, after which a sufficient quantity of very hot glue is poured on one end of the bundle to fill up all the spaces and join the branches together. After the glue has become dry and hard, the bundle is sawn into cross sections of one-half inch thickness.
These cross sections are smoothed down with emery paper and sawn into strips, which are glued on to the window box when forming the panel. The centre of the panel is composed of various kinds of woods, polished to bring out the grain, after which they are inlaid, the spaces between being filled in with glue. Over all, several coats of varnish are applied.
A handsome panel may be made of plaster of Paris. On a sheet of wrapping paper, exactly the size of the panel, draw the design to be worked in plaster.
In mixing the plaster a solution of glue and water is used; the glue is for the purpose of delaying the setting of the plaster, in order to gain time to trim up the plaster when necessary. To the glue and water is added the coloring material. A small quantity of plaster is mixed with the glue water at a time, to the consistency of a thick paste. The plaster is urged from the point of the spoon with which it is applied with a pointed stick that has been thoroughly oiled to prevent the plaster from adhering to it. Some practice is required to guide the plaster so as to keep it within the outlines of the drawing. Another way is to make a coil or cornucopia of stout, well-glazed, and thoroughly greased writing-paper, made small at the point. A quantity of the plaster is placed in the coil, and by gently squeezing the top of the horn a continuous stream is forced out; this may, by moving the horn in straight or curved lines, be made to fill in any pattern drawn. After the plaster patterns have thoroughly dried they are glued in position in the window box and well varnished.
 THE PRINCE'S FIRST RIDE.
THE PRINCE'S FIRST RIDE.
Norwalk, Connecticut.
When I was in Palatka, Florida, last winter, my mamma wrote a letter for me, which was published in Young People. I have always been very much pleased and interested by the children's letters, and have begged mamma to write again for me.
So many have written of their little pets, I want to tell of our little pet robin. It fell from the nest when very small, and we thought it would die; but my auntie made a nest for it in a basket, and fed it often with meal and water, and it grew to be quite tame, and when big enough would eat worms, taking them down whole, until it could hold no more. It would fly across the room, and alight on my auntie's thumb, and stand quietly if she was paring fruit. We were all very much attached to it, and were hoping to be able to have it when a full-grown pet; but one day it flew over a kettle on the stove, and the steam scalded it, though how badly we did not know until it died a week later. We buried it in a little box, and really felt very lonely without it. I now have a pretty Maltese kitten, which, like several other readers of Young People, I have named Toby.
Bertha S.
Monticello, Illinois.
I was visiting in Chicago this fall. I went to the Exposition, and at night I attended the Grand Opera, and saw the electric light. I went to Lincoln Park, and saw a petrified alligator lying on the bank of a pond, with its mouth wide open, and I kept close to mamma till the lady we were with said it was dead. There were two live alligators in the same pond, but they were small ones. I saw a live buffalo. There were some swans there, and I poked my parasol at one, and it ran at me. I saw some panthers and bears, and two sea-lions, which would stick their heads up out of the water, and bark like dogs. A gentleman was pointing at something in the water, and a sea-lion, being hungry, thought he was going to feed it, and it jumped almost out of the water. I went to visit the greenhouse, and there was a parrot which would talk, and a whole cage full of other kinds of birds. I talked to the parrot, and said, "Robin," and it repeated the word after me. Not long ago I saw a letter signed Lena W., and as I have sent two other letters which have not been published, I thought it was my own name until I read the letter. I am ten years old.
Lena W.
Neuchâtel, Switzerland.
There is a very large museum here that was founded by Agassiz. One room is entirely devoted to the fauna of Neuchâtel. Among the animals is a beautiful flamingo, and a very huge wolf and a very small bear. There used to be people here who lived in houses that were built on piles driven into the lake.
A few years ago Lake Neuchâtel was lowered seven feet, and many remains of the lake-dwellers were found. Among them was a boat, supposed to have been used by them. Everything that was wooden when found had turned black, and glistened just like tar.
My sister and I have some Alpine flowers that we would like to exchange for pressed flowers from the Southern, Northern, or very far Western States, but not from Illinois.
Please write before sending, and state whether you want them on cards or not. We do not want ours on cards.
Pressed ferns and small autumn leaves desired, and also maiden-hair ferns.
Kenneth Brown,
Care Messrs. Munroe & Co.,
No. 7 Rue Scribe, Paris, France.
The following two letters are in direct contrast with each other, and are illustrations of the different experiences of exchangers.
Seneca, Kansas.
I wonder if all the boys who patronize the "exchange" column have had the experience I have. I advertised to exchange some pictures I had for stamps, and received about sixty letters. I could exchange with only one, and to the rest I have written, and sent their stamps back. Those six stamps have cost me about two dollars. I think hereafter I will buy what stamps I want. I hope I shall not receive any more stamps.
I enjoy the Young People very much. My papa is a printer, and I have learned to set type. We have fine times going out in the woods after wild plums and grapes.
Paul Wilkinson.
Centre, Alabama.
I have been taking Young People two years. I like it very much. I wait for its coming eagerly every week. There are so many pleasant things with which it is associated. Last spring you published a note from me desiring to exchange. That little note has given me many pleasant moments—I had nearly said pleasant acquaintances. It brought me many letters, from every part of the country. I have answered all, I think. I have yet some quartz crystals, country postmarks in Southern States, strange rocks or petrifactions cut or shaped like iron screws, small cones gathered from swamp pines, to exchange for stalactites, ocean shells, or other curiosities.
Schele De Vere McConnell.
Berkshire, Vermont.
I have had a rabbit die. My sister Flora found it dead. I have a little kitty. It is mine and my little brother's. We have a dog named Rover. I have dug thirty-seven bushels of potatoes this year. My papa is going to pay me for digging them.
I am eight years old. My name is
Samuel Sylvester D., Jun., per Mamma.
Friendship, New York.
I am a little girl of seven. My sister and I have Young People by the kindness of our uncle living in Long Island City. I think Jimmy Brown a funny boy. I cried when Mr. Stubbs was shot. I live on a farm, and have a horse twenty-one years old, which I ride after the cows. Her name is Pet. Our mamma teaches us at home. My sister writes for me. I hope "Tim and Tip" will end well.
Mary C. E.
Pittsfield, New Hampshire.
As so many of the children write about their pets, I think I will write about mine. I have a gray and black kitty which came to us three years ago. When he appeared some one called him Tramp, which made me cry; so mother would not let his name be Tramp, but called him Puffy. Now he is a very handsome cat, and walks in and out in the most dignified manner. I have two snow-white kittens, and I love them very much.
My brother has a dog three months old named Carlo. He is very playful and mischievous, and teases the kittens, until they get out of patience, and give him a cuff on the ear for his insolence. I have also a canary-bird that sings beautifully.
Dearest of all my pets is my horse. His name is Jerry, and I harness him when I please, and some of the rides I take over our beautiful hills and around our little village would do all the young people good. I wish they could ride with me some bright, cool morning. They would return with good appetites for dinner. I am thirteen years old.
Rosa M. F.
Roseville, New Jersey.
I have been spending the summer in Dutchess County, New York. I have a fine Maltese cat whose name is Velvet. I brought him from the country; he weighs ten pounds. I earned the money to pay for Young People by rising at half past five in the morning for seven weeks. I am ten years old. Last year, when in the country, I had eight cats.
We have a baby boy six weeks old named Jasper. He was born on my sister's sixth birthday.
Edna B. D.
Houston, Texas.
We are two little sisters, eight and four years old, and have taken Young People ever since the first number, and enjoy it very much. We liked the story of "Toby Tyler" best of all. "Mildred's Bargain," "The Moral Pirates," and "The Daisy Cot" were splendid, and we look for Jimmy Brown's stories every week. Our baby sister says she likes "Tim and Tip" ever so much.
We have a dear little pet rabbit, some pigeons, and two sweet little calves. We have a doll house and fifteen dolls. We hope our letter is not too long.
Lottie and Lillie.
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
I have just returned from an excursion to Watkins Glen, Niagara, Montreal, Quebec, the White Mountains, and Boston.
I want to tell you about a curiosity which I saw at Watkins, and which amused me very much. It was a blind bat from Havana. The cage was covered with a cloth on which was a label that read, "A blind bat from Havana."
I lifted the curtain expecting to find a great curiosity, but instead of that, I brought to view a brick suspended by a wire from the top of the cage. It was a "brickbat," and it came from Havana, a neighboring town, where there are brick-yards.
C. B. F.
Henrietta, New York.
I have been wanting to write you a letter for a long time, for I see so many letters in the Post-office Box from little girls who are about the same age as myself. I am thirteen years old. I can play on the violin, organ, and piano. All my sisters play the organ also. I have four sisters, two older and two younger than myself. Their names are Fanny, Carrie, Martha, and Alice.
I am learning to ride horseback. Our pony's name is Billy. I do not go to school, and we have had no school since June. We have an aquarium, and in it we have a fish, a bull-head. We have had three mud-turtles. The one we have now is about as large as a silver dollar. I like the story about Toby Tyler and "Aunt Ruth's Temptation" the best. I think "Tim and Tip" promises to be a very good one. I think Jimmy Brown's stories are very funny. I hope he will soon favor us with another story about his misfortunes.
Ella J. N.
Jefferson, Iowa.
I enjoy reading the letters in the Post-office Box very much. I am eight years old. I have no brother nor sister, and no pets except a canary-bird. I go to school, and I have been promoted into the Intermediate Department. My teacher's name is Miss F——, and I like her, though she does give black marks. I haven't had any yet that I know of. When we went to the Centennial Exhibition we visited New York, and mamma, papa, and I went all over Harper's Building, but they didn't print Harper's Young People then. I take music lessons every Saturday. My lesson is in four sharps. I don't like sharps. My music-teacher's name is Mrs. L——, and she intends to teach me a little song when I shall have taken half a term. Mamma says that editors like short letters, so I will stop.
Nettie L. F.
I live at Round Mountain, Alabama. My papa has an iron furnace. It is such a pretty sight to see the iron running into the beds of sand to make pig-iron. I have taken Young People one year, and I like it so much that mamma says I can take it another year. I liked "Toby Tyler" so much, and think "Tim and Tip" is a splendid story. I am eight years old.
Bolling S.
Buffalo, New York.
Two of my little friends have written to this dear paper, and so I thought I would. I live in the city of Buffalo, and I would not change to any other city for anything.
My sister will visit New York this winter, and she is going through the building where Harper's Young People is published; and then I will write another letter, and tell you how she likes it.
I have taken this paper ever since the first number; and even papa and mamma like to read it.
My brother has a piece of wood off Washington's house at Mount Vernon, and a piece of bomb-shell which was thrown from Fort Porter over to Fort Erie; and he has a piece of rope that was cut off the bell of an old Dutch church, New York, at the time of the Revolution. My grandpapa can remember when Canal Street, New York, was nothing but a canal.
Gertrude Hester C.
Several Inquiries.—Harper & Brothers can not bind Young People, but they will furnish a beautifully illuminated cover for thirty-five cents. If by mail, thirteen cents extra. Any book-binder will put it on for you at a trifling expense.
Bertie and Corinne R.—We will publish your exchange as soon as we possibly can; but, dear children, there are ever so many whose exchanges must go in before yours, so be patient. We agree with you both about "Tim and Tip."
G. M.—We would like to see the gray and white kitty, and we think Totty a very pretty name indeed for her.
Frankie D.—If you will write something kind and polite about your sister Emma, we will be glad to print it, but we are afraid, judging from the present letter, that you are very fond of teasing her. You surely do not expect a young lady to be very fond of pigs.
I said last week that I would try to think of some other pleasant evening entertainment for the little club which asked the Postmistress to help them in that way. Here is the game of Rhyming. It may be played by any number of persons. The leader begins by saying to the company, "What do I think of which rhymes with ——?" any word of one syllable which he or she may select. We will suppose the word to be hop. The question will then be, "What do I think of which rhymes with hop?" The person next will then inquire, "Is it an upper surface?" and the questioner will reply, "It is not top." "Is it an undignified movement?" the next may ask, and the answer will be, "It is not flop." "Is it an implement?" somebody else may say, and the reply will be, "It is not mop." And so on, until some fortunate inquirer guesses the word which is in the leader's mind, which may be fop, lop, stop, or any other word which rhymes with hop. This game will furnish a circle of bright young people with fun and good-humored amusement for an hour or two, and will, besides, give them an exercise in definitions which will help to increase their vocabulary.
A Predicament.—The other evening Charlie and I were reading the life of an eminent English artist, David Cox. At one time he gave lessons in drawing, and as his pupils' houses were quite distant from each other, he bought a pony to carry him from place to place. "The pony had previously belonged to an apothecary, and was accustomed to go round with the lad who took out medicines to the residences in the neighborhood. Having been often employed on this business, he knew the connection[Pg 15] well, and did not need to be told where to stop. This knowledge had not forsaken him when Mr. Cox became his owner, and when the drawing-master mounted him to go to his teaching, he fancied that he was taking out medicines still. Accordingly, often during the journey he pulled up short at somebody's door where he had been used to deliver the pills and lotions, and his rider had much difficulty in getting him to proceed. On one occasion Mr. Cox was actually obliged to dismount, hitch the bridle to a gate, and make a pretense of going up to the house, before the pony could be persuaded to budge an inch."
The Postmistress wants you to tell her which English poet it was who wrote the history of a kind of chair. You know chairs have a history, and a very interesting one too. In which of his works can you find the passage referred to? What can you tell about himself, and what were the names of three dear little friends of his who never spoke a word in their lives?
The Postmistress will print in No. 108 the names of all who send answers to these questions. She will also publish the best and most complete answer which she shall receive to these three questions.
K. McD.—To become an expert in the art of illustration, severe and thorough study is the essential thing. You must be an excellent draughtsman, and that no one can become without practice and training. Learn to discipline the hand and to use the eye. Study anatomy, and try to show the varying expressions of the human face, as played upon by passion, sorrow, delight, content, or despair. Endeavor to catch the salient points in a situation, and make a picture which shall emphasize and add to the effect of the descriptive narrative. Your natural talent for sketching will be a great help to you, but nothing will make you really successful except patient and persevering study of drawing, and entire forgetfulness of yourself in your work.
Cohasset, Massachusetts.
Dear Postmistress,—Will you please tell me how to make a leaf album? I have heard of them, and thought I would like to make one, but do not know how.
Could you tell me of some nice books? I like histories ever so much.
I shall be ever so much obliged if you answer my questions in Our Post-office Box.
E. Lulu F.
There are several ways in which a beautiful leaf album might be made. I once possessed one which was composed of card pictures, every one of which represented either a single leaf or a cluster of leaves, with descriptions printed under each picture. A person with skill in painting could make a very lovely album by copying the leaves in their fresh or ripened tints. But probably the best way for you will be to gather leaves and press them carefully, and then fasten them upon your pages either with mucilage or by cutting a little slit in the paper large enough to hold the stem of each leaf. Write under every leaf the name of the species, the place where it grew, and the date of gathering it. You might also write a stanza of poetry on every page, selecting from American or English authors as you prefer. Any blank-book of convenient size will do for an album.
I am very glad you like history. As I do not know what books you have already read, I can give you only the names of some which I like. The Life and Letters of Lord Macaulay, by G. Otto Trevelyan, is a charming biography, and after reading it you will not rest until you have read Macaulay's History of England. Green's Short History of the English People, in one volume, is a book which will charm you from the first to the last page. I hope you read Shakspeare, especially the historical plays. And I advise you to read, by way of informing yourself about American history, Miss Eliza Robins's Tales from American History, and Thatcher's Tales of the American Revolution. Lossing's Field-Book of the Revolution is delightful reading. You will say, "Please, Postmistress, stop," and I will do so, because I might fill a column with the names of books which an intelligent young person would enjoy reading. One thing let me add, and that is, that a good school text-book is always an excellent book to keep at hand for reference when you are reading larger histories.
The careful perusal of Young People will help you to learn about out-of-the-way episodes in history, which you might have to look over many volumes to find.
The following articles in this number are specially designed for the C. Y. P. R. U.: "The Home of the Reindeer" (illustrated), by John Habberton; "Bits of Advice"; and "Window Gardening," with several illustrations.
Contributions received for Young People's Cot in Holy Innocent's Ward, St. Mary's Free Hospital for Children, 407 West Thirty-fourth Street, New York:
Rev. John G. Smith, Chicago, $1; Amy Fownes, Alleghany, 51c.; Annie Rothery, Matteawan, $1.25; D. W. Bishop, Jun., Lenox, 50c.; C. F. Bishop, Lenox, 50c.; Frank L. Cisco, Staten Island, $1; May Cisco, Staten Island, $1; Walter E. Saunders, Washington, N. J., 50c.; Grace C. Hayes, Clinton, N. Y., 51c.; Grace and Willie Fyfield, Yocumville, $2.50; J. Clarke Burrell, New York, $1; proceeds of a fair held by Lulie Lawrence, Lulie H. Fox, Gertrude Birch, Adelia F. Doolittle, Jennie I. Baxter, Josie A. Lawrence, Mamie Doolittle, and Carrie H. Lawrence, of Linden, Montgomery Co., Md., $6.75; Gerald Morton Bliss, East Providence, 27c.; Alma L. and Kleber A. Campbell, West Rutland, Vt., $1; Anna and Levi Rassow, Reading, Penn., $1; Jamie and Freddie Miller, Mamaroneck, $1; Amy Cohen, Albany, 25c.; Willie Needham, New Bedford, Mass., 35c.; Maude and Carrie Cooke, Cheltenham, Penn., $1; Marguerite Laquer, Mendrisio, Switzerland, $2; Dudley A. Williams, Hackensack, 50c.; Allie Bales, Philadelphia, 1c.; A Reader of Young People, Flushing, $1; L. D. C., Chicago, $2; "Little Ada," Cincinnati, 20c.; Hope Kishlar, Goodland, Ind., 50c.; Grace V. C., Watertown, N. Y., 25c.; total, $28.35. Previously acknowledged, $138.61; grand total, $166.96.
E. Augusta Fanshawe, Treasurer, 43 New St.
October 15, 1881.
Goodland, Indiana.
I ride down to the pump on Billy, and lead Charlie. Papa or George pumps the water. I have a tabby cat, but think my Billy horse is the nicest pet. I asked mamma if I could shake some money out of my bank for the Cot. I shook out fifty cents. I was five years old last April. My little playmate, Mamie Harper, is very sick. My aunty wrote this for me. I told her what to say.
Hope Kishlar.
East Providence, Rhode Island.
My little son is very anxious to send his contribution, which he has earned himself, for the Young People's Cot in St. Mary's Hospital, New York. He has just recovered from sickness, is eight years of age, and his name is Gerald Morton Bliss. Wishing you success in your good work, I am, yours truly,
T. A. Bliss.
Alleghany, Pennsylvania.
I am a little girl two years old. I live with my grandparents. My aunt has been telling me about the cot in St. Mary's Free Hospital, and I want to send my money for the poor little sick girls and boys who have nobody to take care of them. My grandpa and grandma give me money, and I put it into a pretty little shell purse I have. I send you all I have in my purse now, and maybe I will send you some more another time.
Amy Fownes + Her mark.
I inclose fifty cents, the contents of my bank, which I wish to give for the Young People's Cot. I work for mamma, gathering up dead leaves, which she pays me for, and I will try and save some more money to send to you before winter comes. I am seven years old, and live in Hackensack, New Jersey.
Dudley A. Williams.
West Rutland, Vermont.
Inclosed find one dollar for the Young People's Cot from Alma L. and Kleber A. Campbell, of West Rutland, Vermont. They were so interested in the account of it they saw in Harper's Young People that they have gladly been without candy to earn the dollar to send.
A. C. Campbell.
Linden, Maryland.
We take the Young People (my two little sisters and myself), and we read in the Post-office Box your letter to the children, asking us to help endow a cot in the little folks' ward, to be called the Young People's Cot. We wanted to do something to help you, so we called our little neighbors together, and read them your letter. We talked it over, and concluded to have a little fair. We did not expect to make much, as there were so few of us; but we did the best we could, and held our little fair Thursday, September 15. We inclose the proceeds, $6.75, hoping it will help you in the good work. It will please us very much, if you have received this, to let us know through the Young People.
Lulie Lawrence,
Lulie H. Fox,
Gertrude Birch,
Adelia F. Doolittle,
Jennie I. Baxter,
Josie A. Lawrence,
Mamie Doolittle,
Carrie H. Lawrence.
New Bedford, Massachusetts.
I have been saving my pennies till I have twenty-five cents, which I send to Young People's Cot. My mother has given me ten cents, making in all thirty-five cents, for which amount you will find stamps inclosed. I have taken Young People nearly a year, and like it very much.
Willie Needham (8 years).
N. B.—The History of a Mountain, by Élisée Reclus, translated by Bertha Ness and John Lillie, and profusely illustrated with fine engravings, will be sent to the boy or girl who shall send the best puzzle to Our Post-office Box between November 1 and December 7. This book is one which will be an addition to any library, and we hope our puzzlers will try to earn it. Obsolete words must not be used in the puzzles submitted for the prize.
Correct answers to puzzles have been received from Alfred C. Gondie, "Dolly Varden," J. Knight Durham, E. E. Steele, George Sylvester, Pansy Elcton, Thecla Clark, Jenny C. Ridgway, Susie M. Farrell, Maggie A. Farrell, Alice M. Southworth, "Queen Bess," W. W. S. Hoffman, Willie Volckhausen, Emma Roehm, G. E. H., J. Marks, Jemima Beeston, Leo Marks, Alice and Katharine, "Lodestar," "Blizzard," Eddie S. Hequembourg, Frank S. Davis, Joseph C. Welch, "Dandy," Henry Elliott Johnston.
| 1.—1. A guide. 2. A boy's name. 3. A gum. 4. Above. 5. A letter. |
| 2.—1. A letter. 2. A nickname. 3. To prevent. 4. A mound of earth. 5. A letter. |
Captain Hal.
1. A letter. 2. Dull. 3. Begot. 4. Forms with lines of differing colors. 5. Appropriate to a siren. 6. Mealy. 7. Painting. 8. To delude. 9. A river. 10. To drag. 11. A letter.
Aerolite.
In virtue, not in beauty.
In play, but not in duty.
In glory, not in fame.
In hero, not in name.
In action, not in deed.
In flower, not in weed.
In flame, not in fire.
In harp, not in lyre.
By whole is the home celestial
Of the brave in battle slain,
Where all is peace and triumph,
And never is sorrow or pain.
Nita.
| I am composed of 21 letters, and am the title of a poem by Bret Harte. |
| My 7, 19, 4 does not mean to sail. |
| My 15, 20, 6, 14, 3 will always prevail. |
| My 11, 10, 12 obscures the sight. |
| My 9, 6, 8 is an orb of light. |
| My 1, 2, 16 is caused by pleasure. |
| My 7, 13, 17, 14 is a time of leisure. |
| My 5, 6, 18 is the nickname of a boy. |
| My 9, 2, 4, 21 sometimes expresses joy. |
Harry Thorne.
1. A letter. 2. An abbreviation. 3. Has beginning. 4. Destroys. 5. A bicarbonate of potash. 6. Decides. 7. Hangers on. 8. Obstinacy. 9. Suitors. 10. An abbreviation. 11. A letter.
Prince Charlie.
Bon, ton, son, con, don, won, yon, eon, ion, non.
Dandelion, Buttercup.
One chill day in the early spring, Mother Nature was very busy. She was looking over her patterns, and thinking what she could procure in the way of new dresses for her children. When she came to think of it, she decided that the old ones were quite pretty enough. "As for Dandelion," she said, "nothing suits her style so well as bright yellow. Larkspur is lovely in blue, and Lilies are queenly in white. The beautiful Rose can wear any color except black, and the Daisy must always appear with a gold centre and white fringe. Clover in crimson or white is equally sweet; and as for dainty Buttercup, she could not tell who loved butter if I dressed her in any other shade than yellow. Late in the season my Morning-Glories—delicate, sweet darlings—will be climbing the fences and garlanding the trellises. They may dress as they please. As for the Dahlias, they always come to Autumn's festival in crimps and tinted petticoats. They are stiff and stately, yet I pardon it, for they are bright, showy creatures, and many people like them. Dearest of all, my Chrysanthemums, in white, crimson, and yellow, will bloom after Blue Gentian, Aster, and Golden-Rod have all faded away at the breath of the frost."
Take care of the pennies, and the pounds will take care of themselves.
Bangor.
[For Exchanges, see third page of cover.]
 Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Here is a curious experiment in equilibrium (Fig. 1), which is easily done. Two forks are stuck into a cork, and the cork is placed on the brim of the neck of a bottle. The forks and the cork form a whole, of which the centre of gravity is fixed over the point of support. We can bend the bottle—empty it even, if it contains fluid—without the little construction over its mouth being in the least disturbed from its balance. The vertical line of the centre of gravity passes through the point of support, and the forks move with the cork, which serves as their support, thus forming a movable structure, but much more stable than one is inclined to suppose. This curious experiment is often performed by conjurers, who inform their audience that they will undertake to empty the bottle without disturbing the cork.
 Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
If a woodcock has been served for dinner, or any other bird with a long beak, take off the head at the extreme end of the neck; then split a cork so that you can insert into it the neck of the bird, which must be tightly clipped to keep it in place; two forks are then, fixed into the cork exactly as in the preceding example, and into the bottom of the cork a pin is inserted. This little contrivance is next placed on a piece of money, which has been put on the opening of the neck of the bottle, and when it is fairly balanced we make it spin round by pushing one of the forks as rapidly as we please, but as much as possible without any jerk. We then see the two forks, and the cork surmounted by the woodcock's head, turning on the slender pivot of a pin (Fig. 2). Nothing can be more comical than to witness the long beak of the bird turning round and round, successively facing all the company assembled round the table, sometimes with a little oscillation, which gives it an almost life-like appearance.
My friend (mountain in Massachusetts) and I, accompanied by a (islands in the Pacific) (river in New York) (Territory in the United States) as guide, started from the little (river in Germany), where we had been spending our two weeks' vacation together, in search of (city in New York); for as (mountain in Massachusetts) said, it would never do to return to the (cape in Asia) without some trophy of our skill and prowess.
Having donned our (river in Scotland) hunting suits, we launched the canoe, and were soon gliding swiftly down the river, through whose (lake in British America) one could distinctly see the (cape in Australia) bottom.
We succeeded in shooting the (city in Michigan) without mishap, though our frail craft bobbed about like a (city in Ireland); and having reached our landing-place, we scrambled up the (town in New Jersey), and came upon what seemed to be the ruins of some old (island in Rhode Island) house.
This we passed, and the hunting ground being now close at hand, we sent the guide forward to reconnoitre, while we patiently awaited his re-appearance.
We had not (island in New York) to wait, for the (Territory in the United States) quickly and noiselessly hastened back to us, and, without speaking, pointed eagerly toward the (cape in Asia), where we could distinctly make out a small group of (river in New York) objects, apparently motionless.
"We are in (city in India)," whispered my friend.
And as the animals seemed to be unconscious of our presence, we crept cautiously through the long grass until we were near enough to get a (island off the coast of Scotland) aim.
I singled out a fine bull, and fired.
With a loud bellow of (cape in Scotland) and (town in Ohio), the animal turned to (river in New Guinea); but quickly reloading, I aimed again, and this second (strait in Australia) was more successful, for, with a bound like a (bay in Australia), he fell dead, while the rest of the herd galloped away in (cape in North Carolina). Our guide uttered a (island off the coast of Scotland) of delight; and as he was provided with (river in Georgia) and tinder, we were soon feasting luxuriously on (city in France) tender (city in New York) steaks. Leaving the larger share of our prize as a feast for the (bay in Massachusetts), we started for home, after fruitless attempts to detach a (cape in South America) from the animal's head.
Enter at the gate, pass to the third space, turn to the left, then make first turn to the right. Turn upward, then to the right, thence downward, thence across to the left until forced to turn upward. Then to the right, then downward. Then to the right almost across the puzzle, upward, to left, and the remainder of the course is easy.
A monkey and a porcupine
Went out to walk one night—
'Twas in September, and the moon
And stars were shining bright—
When, in a garden near the road,
They spied a splendid tree,
As full of peaches, round and red,
As ever it could be.
The topmost branch that monkey reached
In one astounding bound,
And soon the ripest peaches there
Were strewn upon the ground;
And 'mong them rolled the porcupine
With porcupiney skill,
And when he left that spot he bore
A peach upon each quill.

And how they laughed, the monkey and
His very sharp young chum,
When, safe at home, they ate them all!
But soon they looked quite glum;
And ere the night had passed they vowed
They'd never steal again;
For "Oh!" they groaned, and "Oh!" they moaned,
"We've got a peachy pain."

[1] Begun in Harper's Young People No. 101, October 4.